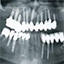
Radiological evaluation of long term complications of oral rehabilitations of thin ridges with titanium blade implants
Submitted: 13 June 2017
Accepted: 13 June 2017
Published: 30 March 2014
Accepted: 13 June 2017
Abstract Views: 485
PDF: 345
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.


 https://doi.org/10.23805/jo.2014.06.01.02
https://doi.org/10.23805/jo.2014.06.01.02







